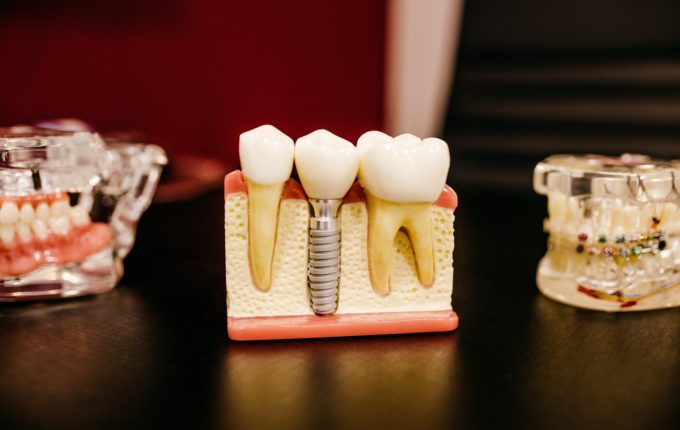
Understanding Tooth Loss and How to Prevent It
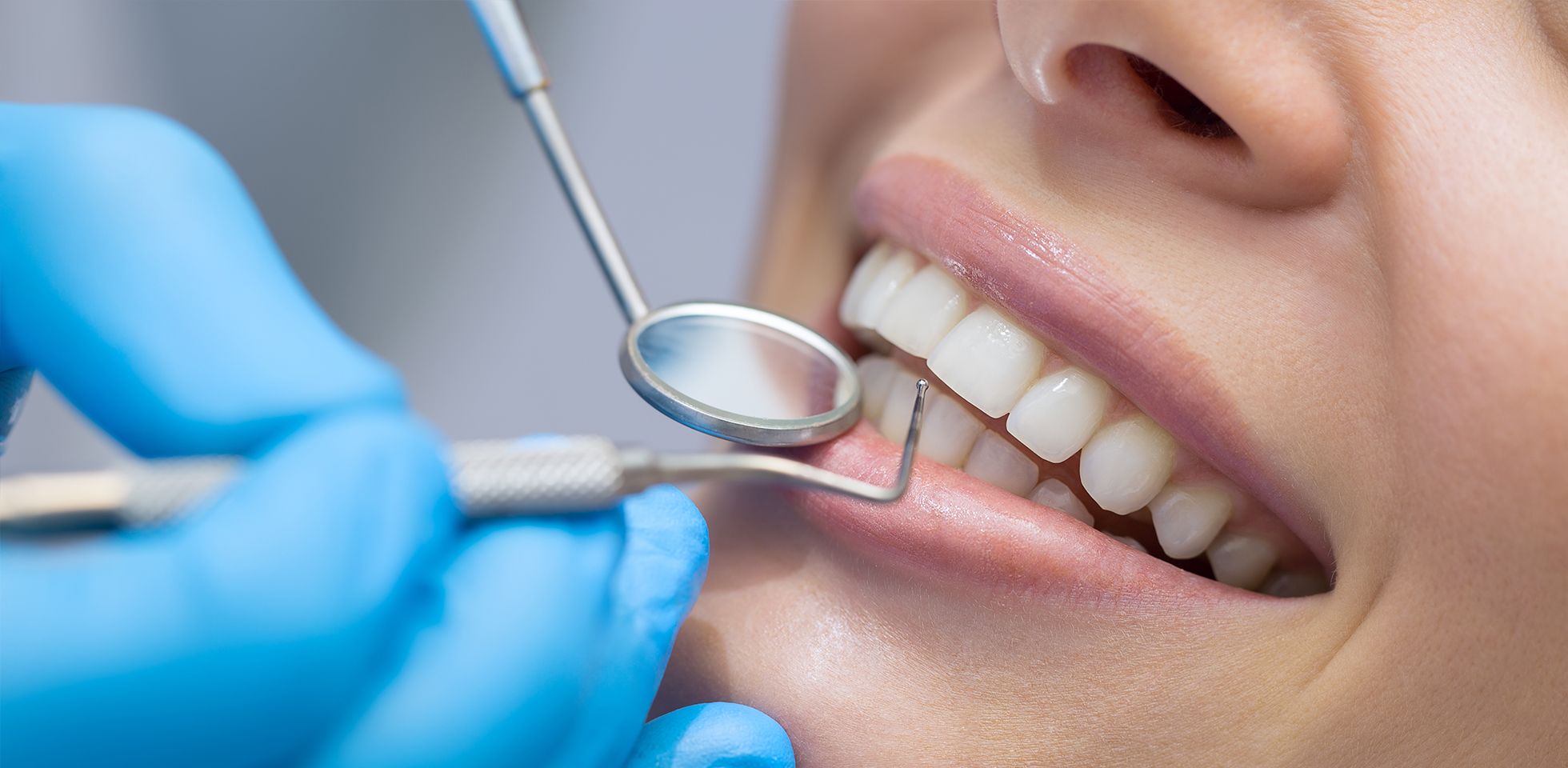
Losing a tooth doesn’t just impact your smile — it can affect your ability to chew, speak and maintain a balanced bite. Studies show that less than half of U.S. adults have kept all of their permanent, and tooth loss becomes more common with age; about 11 % of adults aged 65–74 have lost all their natural teeth and nearly 20 % of those 75 and older are completely. Severe tooth loss (having eight or fewer teeth) affects roughly 26 % of adults aged 65. Many cases of tooth loss are caused by untreated cavities, gum disease or trauma to the mouth. These numbers highlight why timely tooth replacement is so important.
| Teeth Lost | Age Group | Statistical Insight |
|---|---|---|
| 0 (Full Dentition) | Adults 20–64 | ~49% retain all permanent teeth (excluding wisdom teeth) |
| ≤ 8 Teeth Remaining | Adults 65+ | 26% have 8 or fewer teeth remaining (severe tooth loss) |
| All Teeth Lost (Edentulism) | Adults 65–74 | 11% have lost all natural teeth |
| All Teeth Lost (Edentulism) | Adults 75+ | 20% are completely edentulous |
What Are the Most Common Causes of Adult Tooth Loss?
Adult teeth are permanent. If a tooth becomes loose, an underlying cause is to blame. Common causes of tooth loss in adults include:
- Poor dental hygiene: Poor hygiene enables bacteria to build up in the mouth, which can potentially lead to tooth decay and tooth loss if it remains untreated.
- Damaging foods: Sodas, candy and foods with high sugar content are widely known to cause tooth decay. Other potentially damaging foods include bread produced with refined flour, citrus fruits and alcoholic drinks.
- Tooth grinding: Tooth grinding (also known as bruxism) can contribute to tooth loss. Grinding teeth wears away tooth enamel and can crack or chip teeth. Unchecked bruxism can slowly work teeth free from the gums and bone, leading to tooth loss.
- Tobacco use: Smokers lose teeth at more than double the rate for non-smokers. Smokeless tobacco can also cause tooth loss because of tooth decay, gum disease and more.
- Injury and illness: Tooth loss from injury or illness (including gum disease) may happen abruptly or occur over time. In these cases, damage to the surrounding tissue causes the gums to recede and separate from the bone, which can result in tooth loss.
What Happens If You Lose an Adult Tooth?
Adult tooth loss may be gradual or sudden, but if you lose an adult tooth, or more than one, the remaining teeth may start to move. This can cause crookedness as well as potential crowding, depending on where the teeth shift.
Additionally, missing teeth can cause the gums to recede and the jawbone to shrink, which can make the teeth on either side of the missing tooth weaker. It also makes them more susceptible to plaque, decay and gum disease.
Tooth Loss Treatment
Treatment options for tooth loss depend on the cause(s) of tooth loss. To begin treatment, schedule a dental examination. Treatment options include:
- Implants and crowns: These options replace a single tooth. Implants and crowns are both made to match existing teeth.
- Bridges and dentures: While a bridge can be used to replace a single tooth, it also works to replace more than one tooth at a time. Full or partial dentures can also be used when a person has lost multiple teeth.
If gum disease is the reason for your tooth loss, you will also need to work out a treatment plan with your dentist for that as well.
How to Avoid Loosing Teeth and Prevent Tooth Decay
Tooth loss prevention begins with good oral hygiene and regular dental examinations. In many cases, adult tooth loss can be stopped and even reversed with proper and timely dental care. Contact your dentist right away if you notice worsening breath, pain or bleeding in the gums or damage to your teeth.
Brushing, flossing and regular checkups can help preserve teeth for years to come. Mouthguards offer protection from bruxism, and deep cleanings help to prevent tooth decay. For more on tooth loss or to schedule a dental examination, book your appointment online or call us at 212-355-2290 today.
 Our History
Our History
 Our Providers
Our Providers
 About Us
About Us
 Blog
Blog
 Contact us
Contact us
 Diagnostic & Preventive
Diagnostic & Preventive
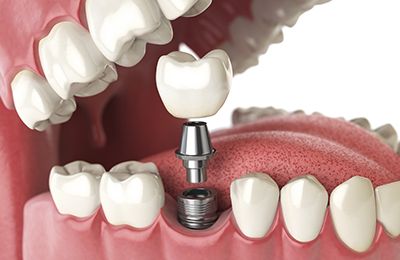 Implant Dentistry
Implant Dentistry
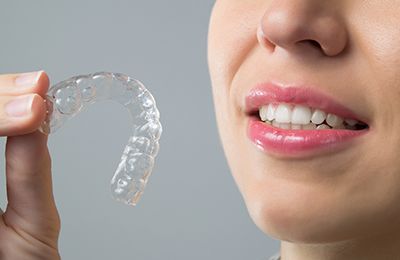 Clear Braces - Invisalign
Clear Braces - Invisalign
 Cosmetic Dentistry
Cosmetic Dentistry
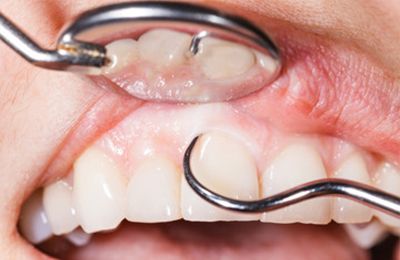 Periodontics
Periodontics
 Patient Forms
Patient Forms
 Payment Information
Payment Information
 Insurance Options
Insurance Options
 CareCredit Dental
CareCredit Dental
 Appointment Policy
Appointment Policy
 Free Consultation
Free Consultation
 Complimentary Teeth Whitening
Complimentary Teeth Whitening
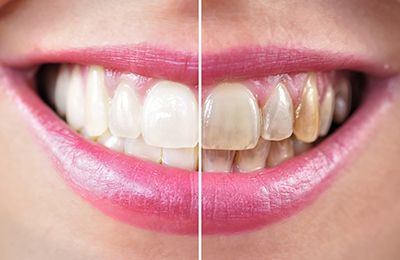 Teeth Whitening
Teeth Whitening